Boiling Point of Ester and Carboxylic Acid
A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen H atom or to some other univalent combining group. NN-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide DCC or DCCD is an organic compound with the chemical formula C 6 H 11 N 2 C.
21 1 Structure And Properties Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Salts Chemistry Libretexts
Why do you wash the dichloromethane solution of your reductive amination product with sodium bicarbonate rather than dilute aqueous HCl.
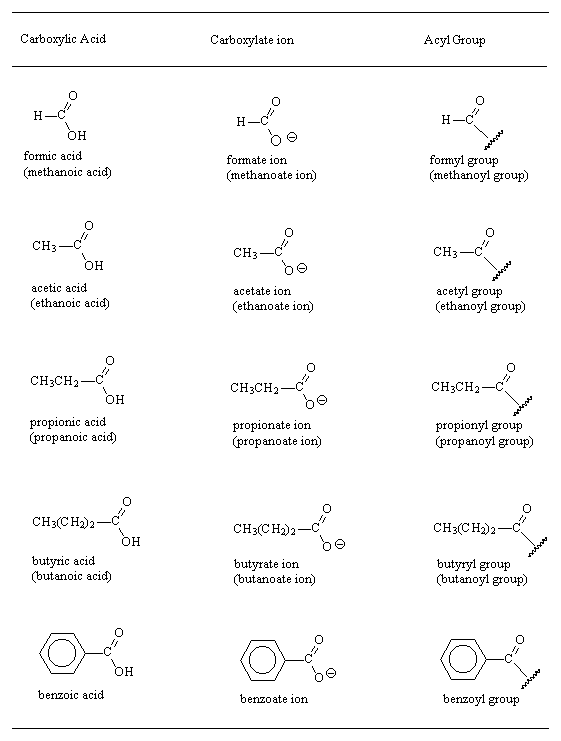
. Students could make soap. COOO-H is a weaker acid than acetic acid as acetate ion is stabilised by resonance. This fusion should be effected in a platinum crucible since phosphoric acid when heated.
A Sodium bicarbonate is a good method of removing aldehydes from organic solventb The amine product will be protonated by acid and remain in the aqueous layer as a saltc Sodium bicarbonate transfers the amine starting. The carboxyl COOH group is so-named because of the carbonyl group CO and hydroxyl group. Carboxylic acid any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon C atom is bonded to an oxygen O atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group OH by a single bond.
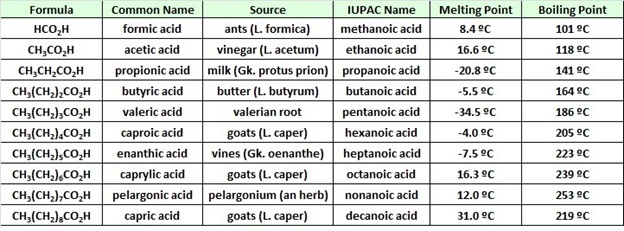
Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH 3 CH 2 3 COOHLike other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids it has an unpleasant odorIt is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis from which it gets its nameIts primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Students could identify an ester by measuring its boiling point followed by hydrolysis to form the carboxylic acid which is purified by recrystallisation and determine its melting point. AT b c d and k.
In general dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acidsDicarboxylic acids are also used in the preparation of. Phosphoric acid is an odourless colourless viscous liquid possessing in a high degree the property of reddening litmus. The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO 2 CRCO 2 H where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.
It cannot be obtained free from water. Its primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesisThe low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor.
When exposed to a red heat and afterward cooled it forms a transparent brittle glass. Acidic strength of aromatic acids The parent member of the family benzoic acid which is a weaker acid K a 63 x 10-5 than acid K a 177 x 10-5 but stronger than acetic acid. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups COOH.
Some order of acidity are b Similarly K a. Salts and esters of valeric acid are known.

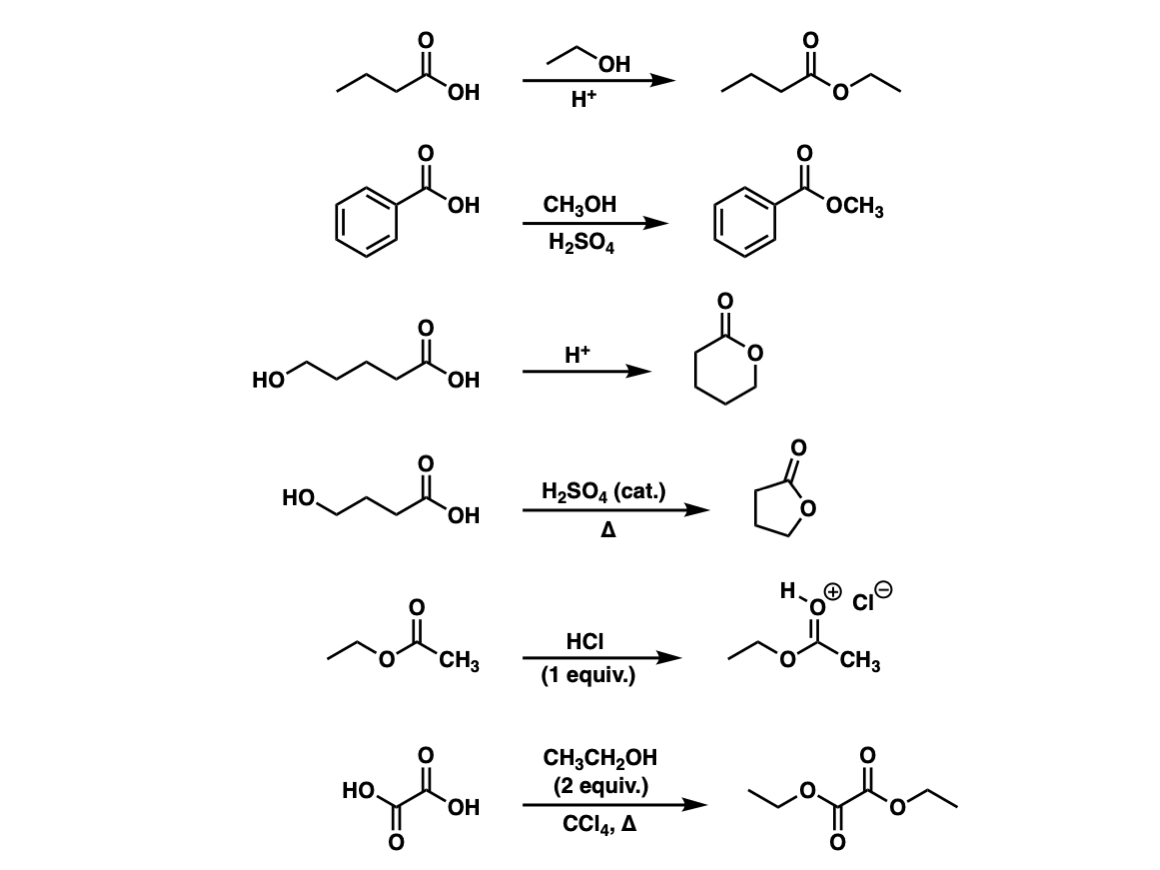
Conversion Of Carboxylic Acids To Esters Using Acid And Alcohols Fischer Esterification Master Organic Chemistry
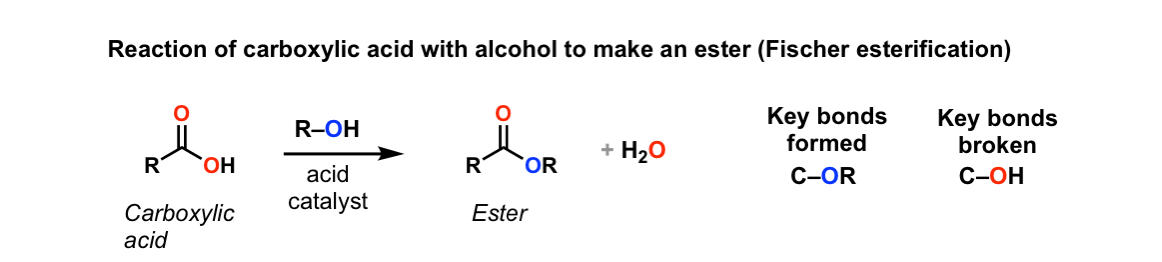
Conversion Of Carboxylic Acids To Esters Using Acid And Alcohols Fischer Esterification Master Organic Chemistry

No comments for "Boiling Point of Ester and Carboxylic Acid"
Post a Comment